Product Name: VEGFR1-pY1053
Product Number: AB-PK851
| Size: | 25 µg | Price: | 89.00 | |
| $US |
Target Full Name: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
Target Alias: FLT; Flt-1; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1; Fms-related tyrosine kinase 1; FRT; Tyrosine-protein kinase FRT; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT; VGFR1; CCDS9330.1; ENSG00000102755
Product Type Specific: Protein kinase phosphosite-specific antibody
Antibody Code: PK851
Antibody Target Type: Phosphosite-specific
Antibody Phosphosite: Y1053
Protein UniProt: P17948
Protein SigNET: P17948
Antibody Type: Polyclonal
Antibody Host Species: Rabbit
Target Alias: FLT; Flt-1; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1; Fms-related tyrosine kinase 1; FRT; Tyrosine-protein kinase FRT; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT; VGFR1; CCDS9330.1; ENSG00000102755
Product Type Specific: Protein kinase phosphosite-specific antibody
Antibody Code: PK851
Antibody Target Type: Phosphosite-specific
Antibody Phosphosite: Y1053
Protein UniProt: P17948
Protein SigNET: P17948
Antibody Type: Polyclonal
Antibody Host Species: Rabbit
Antibody Immunogen Source: Human VEGFR1 (Flt1) sequence peptide Cat. No.: PE-04AGP99
Antibody Immunogen Sequence: NPD(pY)VRK(bA)C
Antibody Immunogen Description: Corresponds to amino acid residues N1050 to K1056; In the protein kinase catalytic domain activation T loop region between subdomains VII and VIII.
Antibody Immunogen Sequence: NPD(pY)VRK(bA)C
Antibody Immunogen Description: Corresponds to amino acid residues N1050 to K1056; In the protein kinase catalytic domain activation T loop region between subdomains VII and VIII.
Production Method: The immunizing peptide was produced by solid phase synthesis on a multipep peptide synthesizer and purified by reverse-phase hplc chromatography. Purity was assessed by analytical hplc and the amino acid sequence confirmed by mass spectrometry analysis. This peptide was coupled to KLH prior to immunization into rabbits. New Zealand White rabbits were subcutaneously injected with KLH-coupled immunizing peptide every 4 weeks for 4 months. The sera from these animals was applied onto an agarose column to which the immunogen peptide was thio-linked. Antibody was eluted from the column with 0.1 M glycine, pH 2.5. Subsequently, the antibody solution was neutralized to pH 7.0 with saturated Tris.This antibody was also subject to negative purification over phosphotyrosine-agarose.
Antibody Modification: Unconjugated. Contact KInexus if you are interest in having the antibody biotinylated or coupled with fluorescent dyes.
Antibody Modification: Unconjugated. Contact KInexus if you are interest in having the antibody biotinylated or coupled with fluorescent dyes.
Antibody Concentration: 1 mg/ml
Storage Buffer: Phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, 0.05% Thimerasol
Storage Conditions: For long term storage, keep frozen at -40°C or lower. Stock solution can be kept at +4°C for more than 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Product Use: Western blotting | Antibody microarray
Antibody Dilution Recommended: 2 µg/ml for immunoblotting
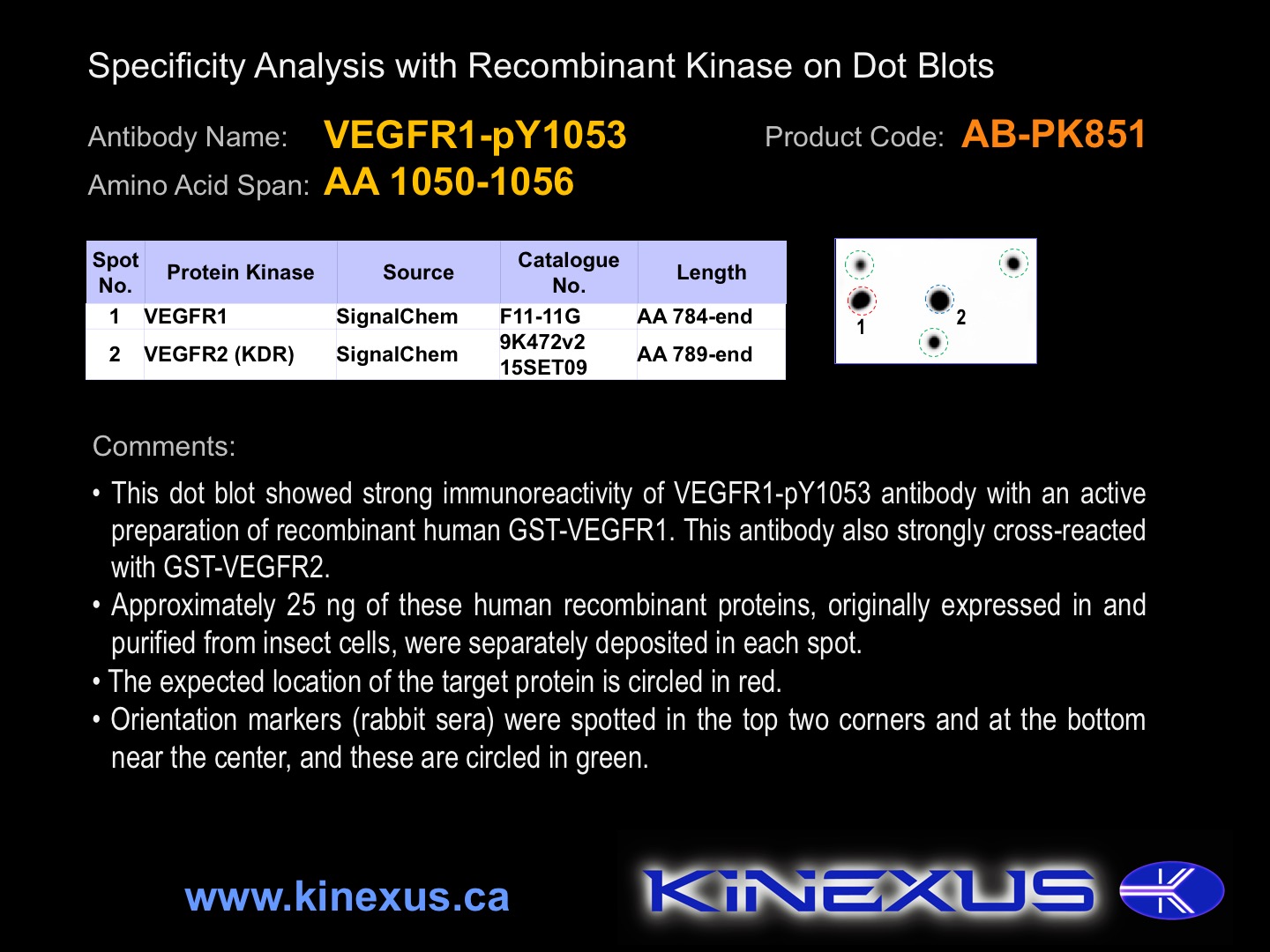
Antibody Potency: Medium-strong immunoreactivity of a target-sized protein by Western blotting in T98G cells. Medium-strong immunoreactivity with recombinant human VEGFR1 on protein dot blots.
Antibody Species Reactivity: Human
Storage Buffer: Phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4, 0.05% Thimerasol
Storage Conditions: For long term storage, keep frozen at -40°C or lower. Stock solution can be kept at +4°C for more than 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Product Use: Western blotting | Antibody microarray
Antibody Dilution Recommended: 2 µg/ml for immunoblotting
Antibody Potency: Medium-strong immunoreactivity of a target-sized protein by Western blotting in T98G cells. Medium-strong immunoreactivity with recombinant human VEGFR1 on protein dot blots.
Antibody Species Reactivity: Human
Antibody Positive Control: The observed molecular mass of the processed target protein on SDS-PAGE gels is reported to be around 150-190 kDa.
Antibody Specificity: High-very high
Antibody Cross Reactivity: Medium immunoreactivity on protein dot blots with recombinant human VEGFR3 and weak immunoreactivity with VEGFR2. No significant cross-reactive proteins detected in MCF7 and T98G cells.
Related Product 1: VEGFR1-pY1053 blocking peptide
Related Product 2: VEGFR1 pan-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-NK226-2P)
Related Product 3: VEGFR1-2 pan-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-NK226-1)
Related Product 4: VEGFR1-pY1048 phosphosite-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-PK850)
Antibody Specificity: High-very high
Antibody Cross Reactivity: Medium immunoreactivity on protein dot blots with recombinant human VEGFR3 and weak immunoreactivity with VEGFR2. No significant cross-reactive proteins detected in MCF7 and T98G cells.
Related Product 1: VEGFR1-pY1053 blocking peptide
Related Product 2: VEGFR1 pan-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-NK226-2P)
Related Product 3: VEGFR1-2 pan-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-NK226-1)
Related Product 4: VEGFR1-pY1048 phosphosite-specific antibody (Cat. No.: AB-PK850)
Scientific Background: VEGFR1 (Flt1) is a protein-tyrosine kinase of the TK group and VEGFR family. It functions as a membrane receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB, and PGF. Binding vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which induces dimerization and autophosphorylation. Autophosphorylation of Y1169 induces interaction with PLCg1. Autophosphorylation of Y1213 increases phosphotransferase activity and induces interaction with Grb2, PLCg1 and SHP2. Autophosphorylation ofY1333 induces interaction with Cbl, Crk, Nck1 and PLCg1. VEGFR1 is critical for the development of embryonic vasculature, angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis, and cancer cell invasion. In adulthood, VEGFR1 promotes endothelial cell proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis. In addition, the VEGFR1 protein mediates the activation of the MAPK and Akt1 intracellular signalling pathways, as well as directly phosphorylates Src, Yes1, and possibly Cbl. VEGFR1 appears to be an oncoprotein (OP). Cancer-related mutations in human tumours point to a gain of function of the protein kinase. Gain-of-function mutations in the VEGFR1 gene are associated with cancer development. VEGFR1 expression has been shown to contribute to cancer cell survival, proliferation, migration, tissue invasion, tumour angiogenesis, and metastasis. In addition, VEGFR1 may promote cancer pathogenesis by enhancing inflammatory responses and recruiting tumour-infiltrating macrophages.
Figure 1. Dot blotting VEGFR1-pY1053 antibody with recombinant purified proteins.
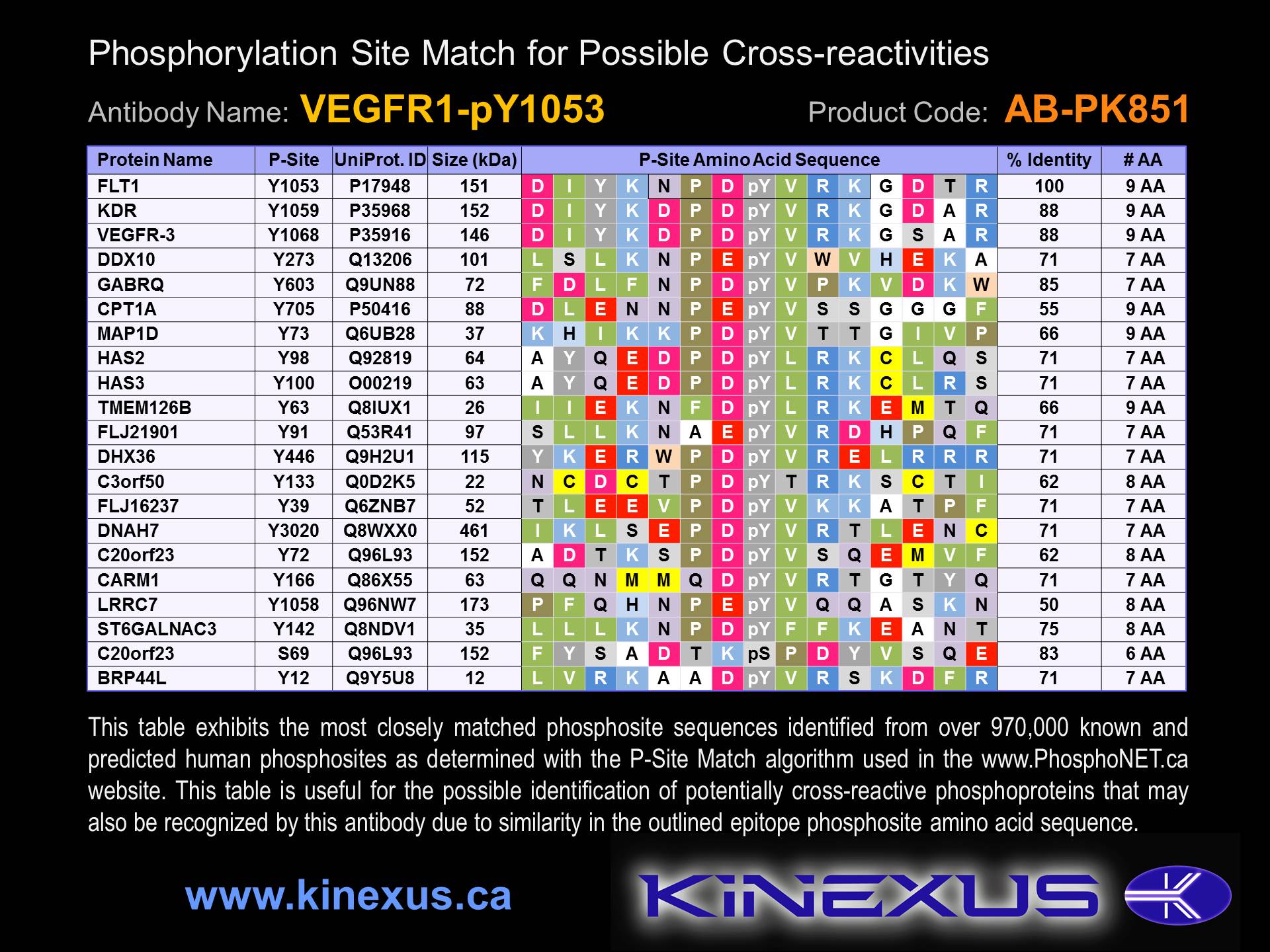
Figure 2. Identification of phosphosites related to VEGFR1-pY1053.
© Kinexus Bioinformatics Corporation 2017